Aliphatic Solvents
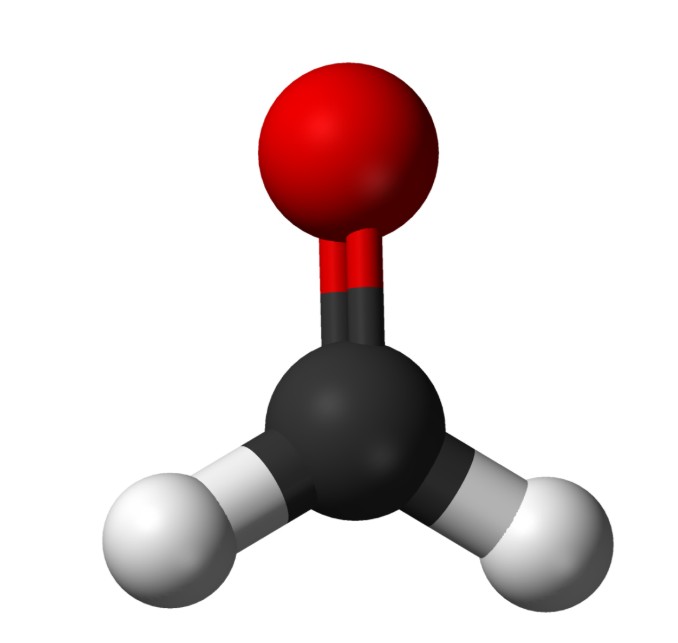
Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde (methanal) is an organic compound with the formula CH2O. It's a pungent, colourless gas that polymerizes into paraformaldehyde and is stored as formalin. As the simplest aldehyde, it is a key precursor in producing resins for particle boards and coatings. Formaldehyde is a classified carcinogen and can cause respiratory and skin irritation.
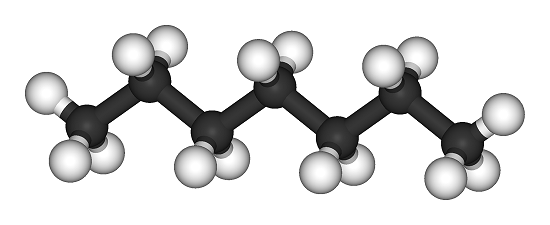
Heptane
Heptane or n-heptane is a straight-chain alkane (C7H16) used in anti-knock engine testing. It represents the zero point in the octane rating scale. This chemical is key in determining fuel performance and is globally used for evaluating gasoline combustion properties.
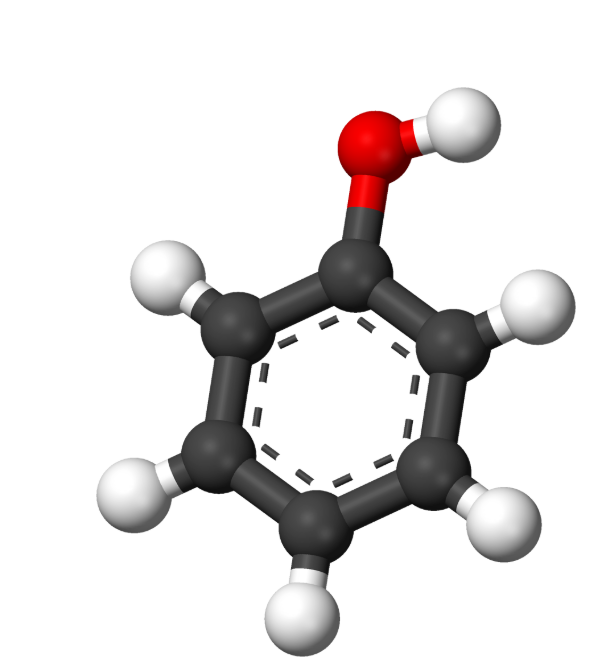
Phenol
Phenol (C6H5OH), also called carbolic acid, is a white crystalline solid with a hydroxy group bonded to a phenyl group. Volatile and mildly acidic, it's primarily used in synthesizing plastics, detergents, herbicides, and pharmaceuticals. Originally extracted from coal tar, modern phenol is petroleum-derived.
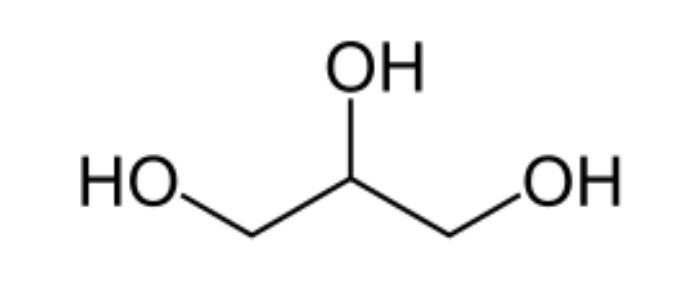
Glycerine
Glycerol (glycerine) is a simple triol that's colorless, odorless, viscous, and sweet-tasting. It's widely used for food, pharmaceuticals, skincare, and medical treatments due to its antimicrobial and hydrating properties. Glycerol is miscible with water and serves as a key compound in lipid chemistry.
